Product Planning
The production planning team is in charge of developing a production timeline and making sure that all requirements for manufacturing and production are met efficiently and cost-effectively.
Related: Production Planner, Production Supervisor, Production Assistant
View all
- Employee Utilization Rate – The percentage of time during which a staff member is actively working versus the number of work hours expected for work (100% utilization means a staff member has no breaks)
- Takt Time – The optimal amount of time required to generate a single item, according to the total available work time and client demand (i.e. the speed of production required to satisfy demand).
- Projected vs. Actual Project Hours – The percentage of work conducted that were either unexpected (i.e., not scheduled) or did not comply with the production plan versus the total number of expected tasks
- Projected vs. Actual Project Hours – The percentage of the difference between hours planned for an employee versus the number of actual hours performed on the floor
- Production Division – A yes/no metric showing whether the firm has different departments devoted on a full-time basis to manufacturing and product assembly
- Product Cost – The average product value to the client at the company manufacturer as determined by the average cost per product unit and average gross margin
- Number of Production Employees – The total number of full-time equivalent (FTE) staff directly engaged in the production tasks of the firm being benchmarked
- Manufacturing & Assembly Groups – A yes/no metric showing whether the product manufacturing and assembly line FTEs are divided between two different groups
- The number of Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) – The total volume of SKUs generated by the firm across all manufacturing facilities.
- Dedicated Production Facilities – A yes/no metric showing whether the firm keeps production centers devoted to manufacturing specific items
- Inventory Turnover – A ratio that indicates how many instances a firm’s inventory is sold and refurbished over a determined time period, which can be measured by dividing the total sales by number of inventory or by dividing the value of products sold (COGS) by average number of inventory available during a specified selling period (monthly, quarterly, yearly)
- Manufacturing Site – Indicates the major factors used by the firm in assigning production across manufacturing centers: manpower costs, regulatory limitations. Distance to clients or suppliers, and others
- Percentage of Spare Manufacturing Capacity – The percentage of manufacturing power assigned by the company manufacturer as spare or excess capacity versus the total manufacturing power
- Capacity Utilization Rate – The percentage of the actual manufacturing yield versus the possible manufacturing yield
View less
Production Objectives
Production objectives are designed to track and measure manufacturing and production efficiencies. Lean production methodologies focus on improving organizational processes and reducing waste in areas like time and raw materials; the more effective the organization, the less the cost of sales and the higher the income generated.
- Improve production count – The production count is defined as the total production over time. This is a standard KPI for a factory floor that tracks and monitors the amount of product created for a specific time frame like a shift, a week, or the last machine changeover.
View all
- Improve the reject ratio – The reject ratio KPI measures the rate of scrap or rejected products versus products sold. The higher the number of rejects, the greater the cost of sales and the lower the profitability levels. The goal is to minimize the amount of scrap created to reach profitability goals.
- Improve rate – The rate KPI measures the speed at which products are manufactured. The slower the manufacturing rate, the greater the cost of sales, and the lower the company’s profitability metrics. Juxtapositionally, if the manufacturing rate is too high, it can affect the quality of the product.
- Improve target – The target KPIs measures the target values that are set for output, rate, and quality. These values encourage employees to reach the set targets for each of these categories.
- Improve Takt time – The Takt time is the amount of time that it takes to complete a task. It indicates the time it takes to manufacture a single product. Or it is the cycle time for a particular operation.
- Improve Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) – The Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) KPI measures whether resources, such as employees and machinery, are being used efficiently.
- Improve downtime – The downtime KPI measures the time that is lost on the manufacturing line due to aspects like equipment failure. It is one of the fundamental metrics to measure. Reducing downtime is a vital goal to achieve and improve on: downtime translates into lost profits.
- Improve Goods Count/Actual Production – The Goods Count/Actual Production KPI measures the number of final products that are ready for sale. This metric is calculated by subtracting the scrapped product figure from the total number of products manufactured. The lower the rejected product numbers versus the total goods manufactured, translates into increased profit.
- Improve availability – The availability of KPI measures and tracks the availability of machines and equipment over time. To achieve optimum production in the factory, the production manager has to ensure that there is the optimal use of all the machines throughout the production line at all times.
- Improve performance – The performance metric measures the overall performance of the machinery. Downtime costs money in that it reduces production capacity. The floor supervisor or floor manager must monitor the performance of the machinery to ensure optimal manufacturing and production levels.
- Improve quality – The quality KPI measures and tracks the quality of the manufactured products over time. In order to guarantee long-term business success and profit, it is crucial to maintain manufacturing quality levels. Maintaining consistent quality throughout the different manufacturing processes leads to the optimal quality of all manufactured products.
- Improve Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) – The Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) KPI measures the overall performance levels of the production floor. The production floor is efficient when employees, machinery, and equipment are functioning optimally. The OEE KPI provides the manufacturer with the necessary information about the overall factory floor’s functioning.
- Improve the behind plan – With the behind plan KPI, management can measure how far the production floor is behind their stated targets and goals. This allows the supervisor to calculate the employee effort levels in relation to their production goals. It is represented as the percentage of actual production versus the expected quantity.
- Improve the manufacturing cycle time – The manufacturing cycle time measures the time it takes for a manufacturing cycle to complete. When the organization ensures an optimal manufacturing cycle time, the cost of sales will drop, and its profitability metrics will increase.
- Improve the throughput – The throughput measures the average number of units produced on a machine, production line, or manufacturing plant over time. It is one of the most straightforward yet most crucial manufacturing KPIs designed to ensure optimal productivity.
- Improve the processing time – The processing time KPI measures the time taken to manufacture finished goods from raw materials.
- Improve the inspection time – The inspection time KPI measures the time spent inspecting raw materials and finished products.
- Improve the move time – The move time metric measures the time spent moving items in and out of the manufacturing area or factory floor.
- Improve the queue time – The queue time metric measures the time spent waiting between activities like inspection time, product manufacturing time, and quality control time.
View less
Manufacturing Engineering
The manufacturing engineering office creates and improves systems such as software applications, procedures, and methods utilized in the manufacturing operation.
Related: Manufacturing Engineer, Manufacturing Process Engineer, Industrial Engineer
View all
- Changeover Time – Calculates the total time it takes to shift a production plant from manufacturing a product to manufacturing a different one
- Manufacturing Uptime – The percentage of time that the manufacturing process is operative (creating products) versus the total available manufacturing time
- Mean Time to Repair – The typical amount of time (in minutes) needed to fix a damaged or broken piece of manufacturing machine
- Time to Convert Customized Solutions – The typical number of months needed to turn a custom-built solution into a regular product offering
- On-Time Delivery to Commit – The percentage of orders that manufacturing and production yields in full and on schedule versus the total number of orders fulfilled
- Customized to Standard Solution Offerings – A yes/no metric showing whether a manufacturer turns custom-built solutions into regular product offerings.
View less
Manufacturing and Assembly
The manufacturing and assembly office is in charge of the construction of finished products.
Related: Manufacturing Technician/Operator, Assembler, Quality Assurance Inspector, Production Associate/Team Member
View all
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) – A calculation of the availability of the production facility (uptime), efficiency, and quality in one metric/KPI that evaluates the total efficiency of the whole production process
- First Pass Yield (FPY) – A measurement of the variance in items produced (output) by a production process versus the items that went into production (input) – i.e., input vs output
- Percentage of Units Reworked – The percentage of items manufactured that are modified for an upgrade or for correcting mistakes made during the manufacturing process versus the total number of items generated by the production team during a specified time period
- Scrap Rate Due to Errors – The percentage of items manufactured that must be disposed of due to product flaws or errors versus the total number of items generated by the production team during a specified time period
- Utilization Rate (Filling Line) – The percentage of the variance between actual and maximum yield being generated on an assembly line or production floor versus the maximum yield
- Labor Cost per Unit Produced (Unit Cost) – The total amount of labor cost needed during a time period divided by the number of well-produced during that period
- Percentage of Prefabricated Parts – The percentage of parts or components used in the manufacturing of a finished item that is pre-produced at a different location versus the total number of parts or components utilized
- Manufacturing Process Cycle Time – The typical number of days from the time the client’s order is received at the right manufacturing center until the merchandise is available for packaging for standard and custom-build merchandise
- Degree of Customization – The percentage of goods that are custom-built to particular customer requirement and need important modifications in the production process
- Dedicated Sub-Component Assembly Location – A yes/no metric showing whether the organization of particular sub-components happens at dedicated manufacturing plants
- Loss of Production Units – Percentage of the projected decline in production due to unexpected production interruptions during the preceding year versus the total planned production
- Production Attainment – Percentage of the production goals accomplished during a specified time period versus the total number of goals for that term
- Customer Lead Time – The average amount of time (in days) from the moment a client places a product order to delivery of the merchandise to the client
- Manufacturing Facility Productivity – Typical number of merchandise units produced every hour within the facility being benchmarked
- Non-Operating Time (NOT) Codes – The number of unique NOT codes utilized by the firm to describe reasons for manufacturing suspension
View less
Facility Management
The facility management office is in charge of the regulation of the quality, safety, and cost of the properties utilized in the manufacturing process
Related: Facility Manager, Safety Manager, Maintenance Technician, Facility Technician, Maintenance Manager
View all
- Manufacturing Site Considerations – A record of the major factors used by the firm in assigning production across production centers: manpower costs, regulatory limitations, distance to clients or suppliers, and others
- Work Organization “5S” Use – A yes/no metric showing whether the manufacturing team practice 5S (sort, straighten, shine, standardize, sustain) as a way to attain workplace coordination and efficiency
- Manufacturing Floor Space Usage – The percentage of the total available production floor space within the manufacturing area that is utilized for machinery, storage, organizing, etc., versus the total amount of available production floor space
- Safety Incidents per Employee – The number of registered safety-related incidents during a specified time period (month/week/year) divided by the total number of staff members working on the production area during that similar period
- Lean Production – A yes/no metric showing whether a manufacturer adopts lean production methods including timely delivery from suppliers and quality control circles
- Number of Manufacturing Sites – The total number of production centers maintained by the firm, local and overseas
View less
Production Facility Manager Job Responsibilities
- Establishes mill schedules and directs plant personnel on a daily basis.
- Interviews and recommends associates for employment – Interviews and recommends associates for employment; conducts performance evaluations and salary reviews for assigned staff and is responsible for the application and enforcement of organizational policies including safety. Also, it monitors plant and equipment maintenance and repair.
View all
- Monitors employee time cards.
- Monitor levels of raw materials and report shortages to Production Manager and Purchasing Supervisor.
- Oversees facility and equipment maintenance including negotiating with contractors, etc.
- Performs job according to pre-established safety, quality, and efficiency standard operating procedures.
- Performs job according to pre-established safety, quality, and efficiency standard operating.
- Responsible for duties of Production Manager in his/her absence.
- Reviews sales and production report to establish priorities for manufacturing.
View less
Operations Manager Job Responsibilities
- Approve weekly hours as presented by Customer Service Mgr & forward to Bookkeeping
- Assist in any other area’s as necessary
View all
- Approve weekly hours as presented by Customer Service Mgr & forward to Bookkeeping
- Assist in any other area’s as necessary
- Assist in purchase of new equipment/trucks
- Assist in setting up of new equipment/trucks
- Attend one community networking function per month
- Commercial job bids
- Develop & emphasize best safety practices
- Ensure office & showroom are neat and clean at all times
- Field staff badging & credentialing
- Handle all customer complaints
- Handle IT troubleshooting
- Handle ordering of uniforms for new field staff
- Handle post install customer service telephone interviews
- Interview, hire and train new employees, or oversee those personnel processes
- Issue & maintain cell phone equipment for all staff
- Issue PO’s as necessary
- Maintain commercial safety accounts i.e. ISNetworld/Browz
- Maintain Home Depot/Clopay install account compliance
- Manage all disciplinary issues of subordinates
- Manage field issues as needed
- Manage staff, reviewing work schedules and assigning specific duties
- Manage technician productivity to meet company goals
- Oversee all activities related to field operations
- Oversee maintenance of building and grounds
- Oversee management of inventory control
- Oversee truck & equipment repairs
- Perform annual evaluations of direct subordinates
- Perform annual government Sam’s site registration
- Perform sales floor work, such as greetings or assisting customers, as needed
- Placement of all field staff job employment ads & Conduct preliminary duties
- Prepare and provide daily & weekly report to management as required
- Process field quotes for technicians
- Procure janitorial, yard & repair services as needed
- Randomly assess schedule for efficiency
- Request insurance certificates as necessary
- Review and process weekly field time cards
- Review previous day productivity
- Schedule monthly safety meetings
- Supervise organization and productivity of warehouse activities
- Supervise technicians, warehouse manager & dispatcher
View less
Production Supervisor Job Responsibilities
- Ability to supervising – Supervisory responsibilities include interviewing, hiring, and training employees; planning, assigning, and directing work; appraising performance; rewarding and disciplining employees; addressing complaints and resolving problems.
- Analyzes and resolves work problems, or assists workers in solving work problems.
View all
- Assists with other duties as directed by the supervisor.
- Compiles, stores, and retrieves production data.
- Conducts annual performance reviews utilizing the PEDS system for direct employees as well as midyear discussions and ongoing performance feedback.
- Confers with other supervisors to coordinate activities of individual departments.
- Develops or revises standard operational and working practices and observes workers to ensure compliance with standards.
- Ensure proper operation of presses and related equipment, requesting maintenance when necessary.
- Establishes or adjusts work procedures to meet production schedules.
- Inspects and approves all press set-ups. Continually monitors press operations including color reproduction, registration, speed, drying, and print quality.
- Inspects finished products to verify conformance to specifications and directs setup and adjustments of machines.
- Inspects machines and equipment to ensure specific operational performance and optimum utilization.
- Interprets and enforces company policies and safety regulations.
- Interprets printing specifications, blueprints, and job orders and assigns to production personnel.
- Maintains time and pressroom records.
- Monitor attendance according to attendance “points” system, utilizing timekeeping software (eTime) and attendance tracking software (Attendance Counts).
- Performs activities of workers supervised.
- Performs job according to pre-established safety, quality, and efficiency standard operating procedures.
- Plans production operations, establishing priorities and sequences for manufacturing products.
- Prepares operational schedules and coordinates manufacturing activities to ensure production and quality of products meets specifications.
- Recommends measures to improve production methods, equipment performance, and print quality.
- Resolves worker grievances or submits unsettled grievances to the Vice President of Operations for action.
- Responsible for the overall direction, coordination, and evaluation of 1-20 employees.
- Reviews production and operating reports and resolves operational, manufacturing, and maintenance problems to ensure minimum costs and prevent operational delays.
- Reviews production orders or schedules to ascertain product data such as types, quantities, and specifications of products and scheduled delivery dates in order to plan department operations.
- Studies production schedules and estimates labor hours required to complete printing jobs.
View less
Technicians and Installers Job Responsibilities
- Accurately fills in the equipment tab in Field Desk Program
- Adheres to scheduled routes
View all
- Communicates clearly and efficiently with customers
- Completes work correctly and efficiently and has minimal callbacks
- Enters accurate notes in the correct format
- Exhibits cooperation and teamwork
- Follows company procedures
- Follows company safety guidelines
- Has accurate timestamps in the Field Desk program as reflected by Fleetmatics Program
- Has safe driving habits as reflected by reports in Fleetmatics
- Installs doors within company guidelines
- Installs operators within company guidelines
- Is on time to work and does not take advantage of the time allowed for each job
- Keeps vehicle clean and organized
- Meets individual production goals
- Meets QB standards
- Neat and clean personal appearance including hair, facial hair, nails, hands, and clothing
- Produces accurate work orders to include all relevant data
- Uses phone and tablet appropriately and stays within permitted usage
- Wears correct uniform and is clean
View less
Warehouse Manager Job Responsibilities
- Assist in any other area’s as necessary
- Complete daily truck stocking activity FiledOps to ensure technician parts usages match FieldOps.
View all
- Control inventory
- Direct warehouse staff on materials to be loaded or on the assembly of items to be prepared for installation
- Ensure warehouse meets all safety standards i.e.walkways clear and free of hazards
- Keep warehouse organized, neat and clean
- Maintain product inventory & count in showroom cabinet
- Match product purchase delivery tickets with PO’s & enter in FieldOps
- Operate forklift
- Order & maintain safety equipment
- Order field & warehouse supplies
- Oversee delivery orders and exchange of product between locations
- Oversee the receipt and dispersal of materials entering the warehouse; help warehouse staff with this task when required
- Perform accurate monthly inventory count and reconcile to FieldOps
- Process RM’s monthly
- Produce reports regularly (in/out status report/ dead stock report etc.) as required by management
- Pull product for field techs daily work
- Receive & unload ODC truck deliveries, verify load sheet/ packing slips with PO’s, log receipts into FieldOps
- Replace monthly sign out sheets & present to Ops Mgr
- Report shortages to plant after truck delivery
- Review paperwork from all deliveries to determine if additional action is required
- RGA’s Liftmaster (over the phone)
- Secure warehouse facilities at the end of each day
- Stock product into the correct warehouse area
- Track & follow up on order for timely delivery
View less
Deliver High-Quality Work
- Effectively deals with conflict.
- Gets involved in making things better.
View all
- Helps others to improve the quality of their work.
- Sets high standards for quality of work.
- Treats people fairly, without favoritism.
View less
Draftsman Job Responsibilities
- 3D Modelling
- Completing full construction drawings & supporting documents.
View all
- Ensure the final design complies with the regulation standard.
- Ensuring rack set updated for current projects.
- General Office Duties e.g. Backup, Site Bags, etc.
- Maintaining Template (Revit).
- Measuring sites & recording in AutoCAD/Revit.
- Meeting Clients and Presenting.
- On target Brand Ambassador (Dress, Attitude, Speaking, etc.)
- Photorealistic rendering.
- Shopfitting Sketches & Drawings.
- Support & Assist to the Design Team.
View less
Print Production Officer Job Responsibilities
- Liaise with sales department to determine customer requirement.
- Create and design print and digital materials.
View all
- Adhere to brand guidelines and complete projects according to deadlines.
- Retouch and manipulate images.
- Use graphic design software and work with a wide variety of media.
- Listen to the client needs and make necessary changes.
- Develop design concepts.
- Assemble final presentation for printing as needed.
- Approve materials, costs, equipment and size of workforce needed.
- Develop a production schedule detailing all tasks and when they should be completed.
- Oversee the quality production of goods with smooth efficient service and proper packaging.
- Troubleshoot non-technical problems that occur during production, including staff shortages and machinery malfunctions.
- Monitors production cost.
- Liaising with technicians to make sure the machines are in proper working conditions.
- Engage in ongoing cost reduction analysis in all areas of the company.
- Monitoring on the use of the Company machines by all the Staff.
- Preparing reports and updating the management on any issues needing attention.
View less
Operations Manager Objectives
An operations manager is responsible for managing the production and distribution of goods and services. The operations manager objectives are designed to measure and track the job roles and efficiencies of an operations manager. The operations manager ensures that the manufacturing and warehousing divisions are functioning optimally.
- Improve the percentage of lost sales to active customers – The percentage of lost sales to active customers KPI measures the ratio of sales that have been lost due to operational inefficiencies versus the total number of sales to active customers. The higher this ratio, the lower the customer sales metrics will be.
- Improve the percentage of processing errors (Operations processes) – The percentage of processing errors (Operations processes) KPI tracks and measures the ratio of process errors versus the total number of operational processes. The higher this metric, the less efficient the operations department is. And the more the operations manager must intervene to get the manufacturing processes back on track.
View all
- Improve the compliance to BOPs (Operations processes) – The compliance to the Bill of Process (BOP) KPI measures and tracks the extent to which the operations manager ensures that the manufacturing and warehousing processes are compliant with the BOP. The higher this metric, the greater the operational efficiencies, and the higher the operations department’s output.
- Improve the percentage of admin credit notes to sales – The percentage of admin credit notes to sales KPI tracks and measures the percentage of admin credit notes issued to the sales department versus the total number of invoices made out to the sales department. The higher this ratio, the more inefficient the operations department.
- Improve the average plant utilization percentage – The average plant utilization percentage KPI measures and tracks the average utilization of the manufacturing plant’s production line over time. The higher this figure, the more productive and efficient the manufacturing plant is.
- Improve the number of reworks (Operations processes) – The number of reworks in the operations processes KPI measures the number of rejected products manufactured during the standard production line that have been recovered and reprocessed. The higher this number, the greater the manufacturing cost savings and the more effective the rework process.
- Improve the percentage rework costs to total costs (Operations processes) – The percentage rework costs to total costs (Operations processes) KPI measures and tracks the total raw materials cost that is added to the production costs, but, it is not part of the Costs of Goods Sold (COGS) percentage. The lower this percentage, the more efficient the company’s manufacturing process.
- Improve the percentage of schedule stability – The percentage of schedule stability KPI measures and tracks the ratio of actual production versus scheduled or planned production. When there is a wide variance between these two figures, there will be a negative impact on inventory levels, sales numbers, and customer service delivery.
- Reduce the average percentage of machine idle time – The average percentage of machine idle time KPI measures and tracks the ratio of average machine idle time versus the average machine uptime over time. The lower this metric, the greater the production line efficiencies and output.
- Improve the average production yield percentage – The average production yield percentage KPI is designed to track and measure the non-defective goods manufactured versus the total number of items produced over time. The higher this metric, the greater the production line’s efficiencies and successes.
- Reduce the downtime percentage – The downtime percentage KPI measures and tracks the equipment, production line, or plant downtime versus the total time that the manufacturing plant should be running. The lower this metric, the higher the manufacturing plant’s availability and productivity figures.
- Improve the Operational Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) percentage – The Operational Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) identifies the percentage of the planned production line that is completely productive. A score of 100% represents perfect production. This KPI measures and tracks the OEE percentage. The higher this metric, the more productive the production line
- Reduce the setup time percentage – The setup time percentage KPI measures the time it takes to prepare the production line’s machinery and equipment to perform its stated task. The longer the setup time, the lower the machine’s output, and the longer it takes to manufacture and individual item.
- Reduce the unplanned downtime percentage – The unplanned downtime percentage measures the incidental production line (or equipment) downtime in relation to the total planned uptime. The higher this ratio, the less efficient the production line, and the lower its output.
- Improve the works orders delivered within the Standard Lead Time percentage – The lead time is the time it takes for a process to complete from its starting time; the shorter the lead time, the more efficient the company’s manufacturing processes. The Standard Lead Time percentage measures the organization’s lead time manufacturing process versus the industry benchmarks.
- Improve the average manufacturing lead time – The average manufacturing lead time KPI measures and tracks the average manufacturing lead time by dividing the total lead time for all the products manufactured by the number of items manufactured during this time. The lower this metric, the more efficient the organization’s production line.
- Reduce the overtime percentage – The overtime percentage KPI is designed to measure the rate of overtime hours versus the number of regular hours for a particular period. The higher this percentage, the more overtime employees have worked, and the less efficient the company’s manufacturing processes.
- Reduce the unplanned overtime percentage – The unplanned overtime percentage KPI measures and tracks the rate of unplanned overtime versus the total number of regular hours worked during the same period. Overtime is expensive, particularly unplanned overtime; the higher this percentage, the greater the production costs. The lower this ratio, the more efficient the manufacturing process.
- Improve the overtime value – The overtime value is the total amount of overtime paid to employees within a specific period. This KPI measures and tracks the overtime value over time. The lower this metric, the lower the company’s production costs. The higher this number, the greater the organization’s manufacturing costs, the lower the profit.
- Improve the schedule adherence percentage – The schedule adherence percentage KPI measures and tracks the ratio between the planned production schedule and the actual manufacturing schedule. The higher this percentage, the more the actual manufacturing schedule is aligned with the planned manufacturing program.
- Improve the first time orders percentage – The first time orders percentage KPI measures and tracks the number of first-time or orders filled for new customers in relation to the total number of orders filled over time. The higher this rate, the more successful the company’s business operations, the greater the topline and bottom line.
- Improve the perfect order percentage – The perfect order percentage or perfect order ratio is defined as the ratio of orders delivered on time versus the total number of orders delivered in the same period; the higher this metric, the greater the manufacturing plant’s efficiencies, and the higher the company’s topline and bottom line.
- Reduce the value of backorders – The value of backorders KPI measures and tracks the total value of backorders over time. The number of backorders translates into the total number of unfulfilled orders. The KPI value is the total backorders multiplied by the total selling price. The higher this figure, the less efficient the manufacturing process.
- Improve the tasks completed by deadline percentage – The tasks completed by deadline percentage KPI measures the ratio between the number of tasks completed by the stated deadline versus the total number of assignments completed during the same time. The higher this percentage, the greater the number of tasks completed within the stated deadline.
- Improve the number of units processed through a bottleneck – The number of units processed through a bottleneck KPI measures the number of products passed through a bottleneck or one process in a chain of operations with limited capacity that reduces or slows down the entire production line.
- Improve the contribution value through the bottleneck – The contribution value through the bottleneck KPI measures and tracks the total value of the units processed through the bottleneck over time: the higher the value of the units passed through the bottleneck, the greater the organization’s topline and bottom line.
- Improve the number of green projects (Operations initiative) – Green projects are sustainable projects that aim to achieve a high-quality manufacturing process while respecting the world’s natural resources. The number of green projects within the organization’s manufacturing operations KPI measures and tracks the number of sustainable projects implemented by the company over time.
View less
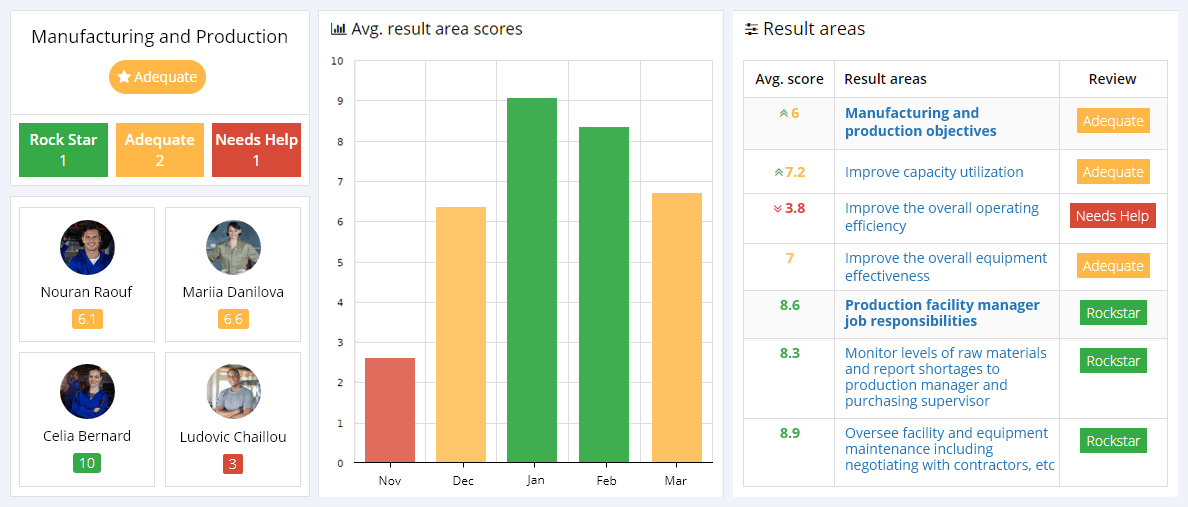
Manufacturing and Production Objectives
Manufacturing and production objectives are designed to track and measure the manufacturing concern’s production output and capacity to increase its production levels.
- Improve capacity utilization – The capacity utilization KPI measures and tracks the manufacturing plant’s available capacity on its production line. The higher this metric, the greater the plant’s ability to increase its production levels.
- Improve the on standard operating efficiency – This KPI tracks and measures the actual operating efficiencies against the labor standards used to cost the product’s manufacturing cost in relation to incentivized production systems. The higher this metric, the greater the operational efficiencies, and the higher employee productivity levels.
View all
- Improve the overall operating efficiency – The overall operating efficiency KPI measures the manufacturing plant’s actual uptime versus the planned uptime. The higher this metric, the greater the company’s productivity, the greater the sales numbers, and the higher the company’s profitability.
- Improve the overall equipment effectiveness – The overall equipment effectiveness KPI tracks and measures how effective the equipment on the manufacturing plant’s production line is. This metric measures both individual machinery as well as all the equipment collectively: the higher this metric, the more effective the equipment, and the greater the production line output.
- Improve (reduce) machine downtime – The machine downtime KPI tracks and measures the overall downtime per machine. It includes both scheduled and unscheduled downtime for maintenance, setups, and machine changeovers. The higher this metric, the lower the machine’s productivity output. The lower this figure, the higher the machine’s output.
- Improve (reduce) unscheduled downtime – Downtime is the time that a production line machine is down. Equipment is shut down at times for maintenance and setups. This is planned downtime. Unscheduled downtime is unplanned downtime, and the longer the machine is down, the lower the productivity metrics. This KPI tracks and measures the unscheduled downtime.
- Improve (reduce) machine set up time – Production time is lost due to setups and changeovers. This metric tracks and measures the production time lost as a result of the time it takes to change dies and set up the machine. The lower this metric, the shorter the setup time, and the higher the machine’s productivity levels.
- Improve inventory turnover – Inventory turnover is the ratio demonstrating how many times the company has sold and replaced its inventory over time. This KPI tracks and measures the manufacturing company’s inventory turnover during a given period. The calculation helps businesses make better pricing, manufacturing, and marketing decisions.
- Improve inventory accuracy – Raw materials are critical components of the manufacturing process. And inaccurate inventory levels This KPI measures and tracks the extent to which the company’s inventory levels are accurate. The greater this metric, the lower the downtime while waiting for raw materials to arrive, and the higher the company’s productivity levels.
- Improve quality – High-quality products are critical to a successful manufacturing company. The higher the quality, the greater the product sales. This KPI tracks and measures the extent to which the manufacturing company produces high-quality products.
- Improve First Pass Yield (FPY) – The First Pass Yield (FPY) KPI tracks and measures the percentage of products manufactured the first time correctly round in relation to the total number of products manufactured over time. The higher this metric, the greater the company’s output, and the higher its bottom line.
- Improve (reduce) rework – Rework is defined as the need to send a product through the production line more than once. There is no greater waste of time and raw materials than rework. This KPI tracks and measures the rework ratio in relation to the overall number of products manufactured in a given period.
- Improve (reduce) scrap – The cost of raw materials plays a fundamental role in the manufactured product’s price. The cost of scrapped raw materials drives up this figure. The greater the scrap, the higher the end product’s priceThis KPI tracks and measures the ratio of scrap versus the total raw materials used over time.
- Improve (reduce) failed audits – Quality control audits are critical in ensuring that the products manufactured and shipped meet the minimum quality control standards. The failed audit KPI tracks and measures the number of failed quality control audits just before the shipment is about to leave the factory.
- Improve the On-Time Delivery (OTD) – The On-Time Delivery (OTD) KPI tracks and measures the percentage of deliveries shipped on time versus the total number of deliveries shipped from the manufacturing concern. The higher this metric, the greater the company’s productivity levels, and the higher the customer satisfaction metrics.
- Improve (reduce) customer returns – The customer returns KPI tracks and measures the number of products returned by customers versus the total number of products shipped. The higher this metric, the lower the customer satisfaction, and the lower the company’s sales numbers and productivity metrics.
- Increase training hours – Training is an essential component of a successful manufacturing company. It teaches employees how to use production line machinery effectively, reducing scrap and increasing engagement and productivity. This KPI measures and tracks the hours employees spend in training in relation to their total hours worked over time.
- Improve (reduce) employee turnover – Employee turnover is the ratio of employees who leave the company versus the total number of employees in a given period. This KPI tracks and measures the employee turnover ratio over time. The lower the metric, the more engaged and productive employees are.
- Improve (reduce) reportable health and safety incidents – Reportable health and safety incidents are any incidents that injure or result in employee loss of life on the factory floor. This KPI tracks and measures the number of reportable health and safety incidents over time. The aim is to achieve zero incidents within a given period.
- Increase revenue per employee – The revenue per employee ratio is the income that each employee generates over time. This KPI is designed to track and measure the income per employee rate over time. And it is calculated by dividing the total revenue for a given period by the number of staff employed during the same period.
View less
The production planning and management of Key Performance Indicators are a vital aspect of organizational success for the manufacturing concern. Tracking KPIs real-time adds further value to this process as it prevents negative short-term trends from evolving into major crises.
Manufacturing KPIs include all aspects of the product lifecycle from its design, prototype development and adoption, the management of product development timeline, the manufacturing and production capacity utilization rate, machinery set up and maintenance, reduction of machine downtime and optimization of machine uptime, health and safety best practices, employee training, product quality control, facility management, and product packaging and dispatch.