General
General supply chain KPIs include metrics such as inventory turnover, order cycle time, order accuracy, delivery performance, and supplier lead time. These KPIs help measure the efficiency and effectiveness of the overall supply chain process.
- Supplier Use – Average number of dealers used by the manufacturer to deliver raw materials to factories.
- Percentage of Raw Materials – Approximate percentage of raw materials obtained by the company factories from the following dealers.
View all
- Distance from Suppliers – Average number of miles between partner manufacturing sites and their key dealers.
View less
Vendor Identification & Management (Qualitative)
Vendor Identification & Management (Qualitative) KPIs include tracking and measuring vendor performance, evaluating vendor compliance with contracts, and monitoring vendor quality and safety standards. These KPIs help to ensure that the organization maintains high standards in its relationships with vendors.
- The Vendor Identification and Management team selects and hires suppliers by examining the price and quality of their products and compare them to the specific criteria.
- Relate: Vendor Relationship Manager, Vendor Management Analyst, Vendor Performance Manager.
View all
- Vendor Evaluation Criteria – Principal standards used by the firm to when picking raw material dealers.
- Vendor Selection Responsibility – Administrative level within the firm with ultimate authority to pick raw material dealers.
View less
Vendor Identification & Management
- New Vendor Setup Cycle Time – The average amount of time required to authorize and add a dealer into the vendor management or procurement system utilized by the firm.
- Percentage of Sole-Source Vendors – Percentage of dealers utilized by the producer that are single-source vendors.
View all
- Cost of Sole-Sourced Material- Expense paid for single-sourced raw materials.
- Percentage of On-Time Deliveries – Percentage of dealers utilized by the producer that are single-source vendors.
- Vendor Certification Requirements – A principal standards used by the firm on vendor accreditation.
- Time Required to Certify Vendor – Average number of months needed for the firm for vendor accreditation.
- Vendor Certification Responsibility – Executive level within the firm in charge of performing and handling vendor accreditation processes.
- Actual vs. Quoted Lead Time – The difference between the delivery time cited by the vendor and the actual delivery time for one order or a set of orders.
View less
Vendor Compliance & Audit
The vendor compliance and audit team is responsible for assessing vendor performance and ensuring that vendors adhere to company and industry regulatory requirements, evaluating vendor specifications, and addressing any issues that may arise. This ensures that vendors meet or exceed quality, safety, and ethical standards.
Related: Compliance Specialist, Procurement Agent, Procurement Specialist, Procurement Compliance Specialist.
View all
- Vendor Performance Measures – Principal standards employed by the producers to assess the performance and service levels given by the dealers.
- Frequency of Evaluation – Frequency with which raw material providers are officially assessed by the firm.
- Vendor Delivery Performance: Average – Percentage of total deliveries received from a regular vendor that meet the requirements for on-schedule delivery and the exact quantity.
- Vendor Delivery Performance: Best Vendor – Percentage of total deliveries received from a leading vendor that meet the requirements for on-schedule delivery and right quality.
- Vendor Delivery Performance: Worst Vendor – Percentage of total shipments received from the worst vendor that meet the requirements for on-schedule delivery and right quality.
- Average Received Materials Test Cycle Time (Days) – Average number of hours needed for the firm’s Quality Management office to complete inventory of incoming materials before releasing for internal usage.
- Acceptance Rate of Inbound Materials – Average percentage of total materials received from dealers that are certified by Quality Control on initial entry.
- Non-Acceptance Rate – Total frequency with which supplies or raw materials are declined by the firm’s manufacturer because of flaws in delivery or irregularities.
- Percentage of Certified Vendors – Percentage of the overall number of dealers that are accredited by the procurement team; subdivided by local/international dealers.
View less
Strategic Sourcing (Qualitative)
The strategic sourcing team is responsible for establishing and implementing procurement policies and procedures that promote efficiency and cost savings in the organization’s purchasing activities. They are also accountable for streamlining the purchasing process to ensure that it is effective and sustainable over time.
Related: Strategic Sourcing Analyst, Sourcing Analyst Specialist, Manager of Purchasing & Strategic Sourcing.
View all
- Budgeting Authority – Executive level within the firm at which budgeting for pre-manufacturing expenses is established.
- Procurement System – Systems used by the manufacturer to record materials acquisition and production planning.
- The extent of Electronic Links – Percentage of dealers that are electronically connected to the producer.
- Use of Electronic Links – Duties the firm’s manufacturer routinely completes through electronic channels.
View less
Logistics Management
The procurement logistics team works in collaboration with suppliers to ensure the timely and efficient delivery of purchased items, meeting the organization’s demands and requirements. They aim to optimize the entire procurement process from sourcing to delivery.
Related: Supply Analyst, Procurement Manager/Director, Procurement Analyst, Procurement Specialist.
View all
- Inventory Turnover -An estimation of how fast inventory is sold and transferred from the storage house to customers or merchandisers.
- Average Shelf Life – Shows the average amount of time that items are kept in the firm’s storage house before they are utilized in the manufacturing process.
- Inventory Accuracy – An estimation of the validity of warehousing statistics relevant to in-stock inventory level. High inventory accuracy enhances customer services, removes wasted time.
- Carrying Cost of Inventory – The expenses needed to store and deliver an inventory of a particular product during a specific term. Expenses include storage house labor, insurance, tax, storage, loss of value, and delivery costs.
View less
Procurement and Logistic Officer Job Responsibilities
Procurement and logistic officer KPIs include tracking operational efficiencies such as reducing procurement costs, ensuring timely and accurate deliveries, improving inventory management, minimizing lead times, and maintaining effective relationships with suppliers.
- Source and buy products for use and for sale in the Company.
- Monthly stock taking.
View all
- Managing the company’s store and distributing material according to usage.
- Keeping records of company stock and recording stock in and stock out. Reviewing the supply chain to ensure it is efficient and effective.
- Managing of personnel records e,g leave days, off days/sick offs, absenteeism, and late coming in accordance with the Human resource manual and filing of the same.
- Organizing and scheduling of office meetings in a timely manner.
- Receiving complaints from personnel and arbitrating where possible.
- Get updates from suppliers on price changes and availability of items.
- Provides logistical support for project activities which includes picking and delivery of client goods and purchased stock in a timely manner.
- Ensuring sound partnership with suppliers.
- Ensuring timely, efficient and effective procurement of goods, services and works, while strictly adhering to the procurement policy.
- Establishing in liaison with the relevant departments and end users, quality specifications of goods and services.
- Carrying out designated checks on quality.
- Managing disposal of obsolete and disposable items with authorization from the management team.
- Preparing reports and updating the management on any issues needing attention.
View less
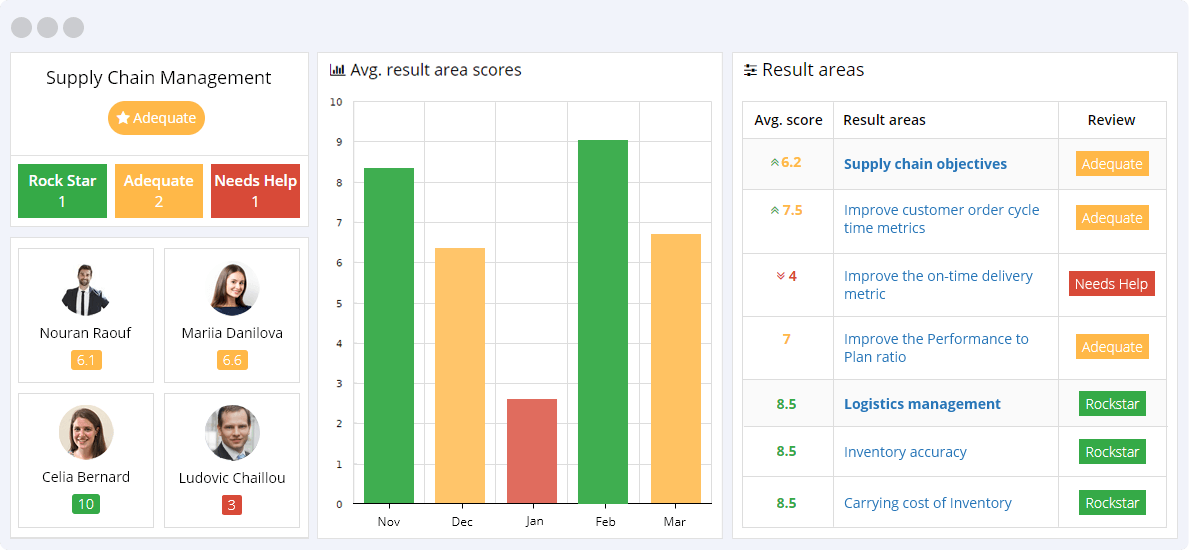
Supply Chain Objectives
Supply chain management is integrated planning, implementation, and control of the flow of products, information, and money across the supply chain from the manufacturer to the end consumer. Supply chain management KPI objectives are designed to assess and monitor supply chain efficiencies, ensuring that end-to-end processes run smoothly and optimally.
- Improve customer order cycle time metrics – One of the company’s fundamental aims is to decrease the amount of time between the placement of a purchase order by a customer to the complete fulfillment of the request. This metric is tracked so that the company can gauge how well it is meeting this requirement.
- Improve disruption impact metrics – Disruption impact is the impact of a natural disaster, political event, and global pandemic on a company’s supply chain processes. Companies must design and implement a disaster management plan to mitigate the disruption of the supply chain so that the customers can still receive the goods they purchased on time.
View all
- Improve conversion rate metrics – Lead acquisition and management are some of the core business functions of a successful supply chain organization. Tracking and improving the conversion rate metrics is an essential element of the successful supply chain business so that your business keeps on moving forward and growing.
- Improve inventory days of supply metrics – The Inventory Days of Supply metric aims to ensure optimal inventory levels at all times. It measures the average time it takes for a company to move its total inventory and provides supply chain managers with the average inventory shipped per day in relation to the inventory on hand.
- Increase quality assurance time metrics – The quality assurance (QA) time metric measures how long it takes your company to complete its quality assurance life cycle. This life cycle must be as short as possible. If this life cycle is too long, it will impact negatively on customer delivery time and customer satisfaction ratings.
- Improve the On-Time Delivery metric – The On-Time Delivery (OTD) KPI measures how many deliveries the number of on-time deliveries. The more deliveries that are completed on time, the greater the customer satisfaction and productivity metrics.
- Improve the Total Delivered Cost metric – The Total Delivered Cost (TDC) metric is the total amount of money that it takes to manufacture and deliver a product. Elements such as operating costs, demand variability, inventory numbers, and supply variability must be taken into account for the calculation of this figure.
- Increase customer service metrics – The customer service KPI is an essential number to monitor and track. The higher the customer service metric, the greater the company’s profitability. High customer satisfaction ratios translate into more business for the company, resulting in increased growth and profitability.
- Improve supply variability metrics – The supply variability is the difference between the demand forecast projections and the quantity of a particular product that is shipped. Therefore, to improve the supply variability metric (or KPI), companies must increase the demand forecast projections versus the shipped product metrics.
- Improve demand variability metrics – The supply chain demand variability measures the fluctuation in customer demand. It is the projected demand versus the concrete demand and a primary inventory management KPI for the supply chain industry. In order to ensure proper inventory management, the forecast demand versus the actual demand figures must be similar.
- Improve operating costs metrics – The operating costs of a company include distribution and procurement costs, warehousing, transportation, and manufacturing costs. This KPI measurement aims to reduce the organization’s operating costs and to increase the company’s net profit.
- Improve the Performance to Plan ratio – The Performance to Plan KPI measures how well the company has adhered to its procurement, manufacturing, distribution, warehousing, and transportation schedule. In other words, this metric determines how well the organization has implemented its operational plans. This metric aims to increase the effectiveness of the Performance to Plan ratio.
- Improve inventory metrics – The Inventory metrics KPI includes “everything inventory.” This metric tracks and measures the overall inventory management, including total inventory, inventory turns, record accuracy, obsolete inventory, working inventory, non-working inventory, and item availability.
View less
Purchasing Department Objectives
Procurement KPIs, also referred to as purchasing objectives, track the efficiency of the procurement department’s business processes. They provide management with valuable insights to streamline acquisition processes, improve efficiency, and maximize ROI on all purchases.
- Increase cost savings – The cost savings KPI measures the extent to which the purchasing department can save on the cost of purchased items. The higher this metric, the more successful your procurement strategy.
- Improve cost reduction – The cost reductions KPI measures and tracks the purchasing manager’s ability to negotiate better prices on products and services. It also measures the purchasing department’s ability to improve operational efficiencies, such as reducing labor costs by streamlining and optimizing processes.
View all
- Improve cost avoidance – The cost avoidance KPI measures and tracks future savings on the purchase of products and services. The higher the cost avoidance metric, the greater the long-term cost savings.
- Reduce maverick spend – The maverick spend KPI measures the total value of all unstructured purchases that have bypassed the internal procurement processes. A high rogue spend amount costs the business a lot of money in unexpected expenses. The lower this metric, the more control the purchasing department has over its procurement processes.
- The total spend per vendor – The total spend per vendor KPI tracks and measures the number of suppliers and the spend per supplier that the procurement department depends on.
- Improve the procurement ROI – The procurement ROI measures and tracks the Return on Investment (ROI) on goods and services purchased. It is used to determine the profitability and cost-effectiveness of the procurement processes. The higher this value, the more successful the purchasing departments procurement processes are.
- Reduce the purchase order cycle time – The purchase order cycle time KPI measures the total time it takes for a purchase order to be sent to a supplier from the starting point. The lower this metric, the quicker it takes to complete the purchase order process, and the more effective and agile your organization is.
- Improve contract compliance – The contract compliance KPI measures the extent to which the purchasing department adheres to its internal processes. The closer to 100 percent compliance, the more accurate the acquisition processes are, and the greater the procurement department’s successes.
- Improve delivery time – The delivery time KPI measures how well the purchasing department functions when it comes to sourcing goods that the business organization needs, within budget, and on time. The lower this metric, the more successful the procurement department.
- Improve cycle time – The cycle time KPI measures the average time spent between the moment when the requisition from another department is submitted and the purchase order placement. In other words, this metric measures the time the purchasing department takes to fulfill the organization’s needs.
- Improve supplier lead time – The supplier lead time KPI measures the average time it takes from the supplier order placement date to the delivery date and time. The lower this metric, the more efficient the procurement department’s processes are.
- Improve the quality standards – The quality standards KPI measures the extent to which the goods purchased fit the company’s requirements. The lower this metric, the more inefficient the purchasing department’s processes. And the higher this figure, the more efficient the procurement department’s operations.
- Reduce inventory risk – The inventory risk KPI measures the risk the company takes when purchasing large amounts of inventory. Suppose the products sell too slowly or too much stock has been purchased. The company runs the risk of reaching the stock’s expiry dates: the lower this metric, the higher the purchasing department’s efficiencies.
- Increase employee learning – The employee learning KPI measures the extent to which employees are striving to improve their work quality and efficiency rates. The higher this metric, the more efficient the purchasing department’s operations and the higher the quality of work that will be delivered.
- Reduce the unit cost per product – The unit cost per product is part of the formula for calculating its sales price. This KPI measures whether the cost per unit rises above the average unit cost. If so, the product’s profit margin is decreased. The higher this KPI, the less profit the company will make.
- Using quantity as a supplier measurement – The using quantity as a supplier measurement KPI measures supplier consistency. The greater the number of incorrect items delivered than the purchase order numbers, the lower the purchasing department’s efficiencies. The lower this ratio, the more efficiently the procurement department can meet the organization’s needs for goods and services.
View less
Supply Chain Management KPIs or Key Performance Indicators are designed to measure the optimal functioning and success of the organization’s ability to manage and purchase raw materials, products, and other supplies needed for the business to function. Within this department, the critical performance areas that must be measured are the effective management of suppliers including vendor identification based on raw material cost, ability to deliver on time, and quality of raw materials, vendor compliance, and logistics management.
Continuous KPI tracking enables management to identify contradictory short-term trends to take proactive measures to rectify these tendencies before they evolve into production-stopping disasters.