Asset Manager Job Objectives
Banking key performance objectives are designed to monitor and manage the success of the organizational unit. Progress in aspects like the operating profit per employee, the total number of assets managed per employee, and the overall sales per branch are essential metrics to track to ensure the bank’s operational success.
- Improve revenue levels – Banking revenue is defined as all incoming cash flow. This can be broken down into categories like total revenue by deposit interest, loan interest, service fees, and transaction fees. Banks need this revenue to fund their business operations. It is essential to increase this metric over time consistently.
- Improve expense metrics – Banking expenses include all of the costs generated during bank operations. They are divided into two categories: interest and noninterest fees. And the higher these costs, the lower the bank’s net profit. It is essential to monitor and track these expenses to ensure that they remain at an affordable level.
View all
- Improve operating profit – Operating profit is the income generated from the company’s core business operations. In its simplest form, this figure is achieved by subtracting total expenses from total revenue. The operating profit KPI monitors and tracks the operating profit levels between measurement periods. And it is critical that this metric keeps increasing.
- Improve Operating Expenses As a Percentage Of Assets – The total operating expenses as a percentage of assets is calculated by dividing the total operating expenses by the total dollar amount of owned assets, shown as a percentage. This percentage demonstrates how much the assets cost or how it measures what the bank is spending to manage its assets.
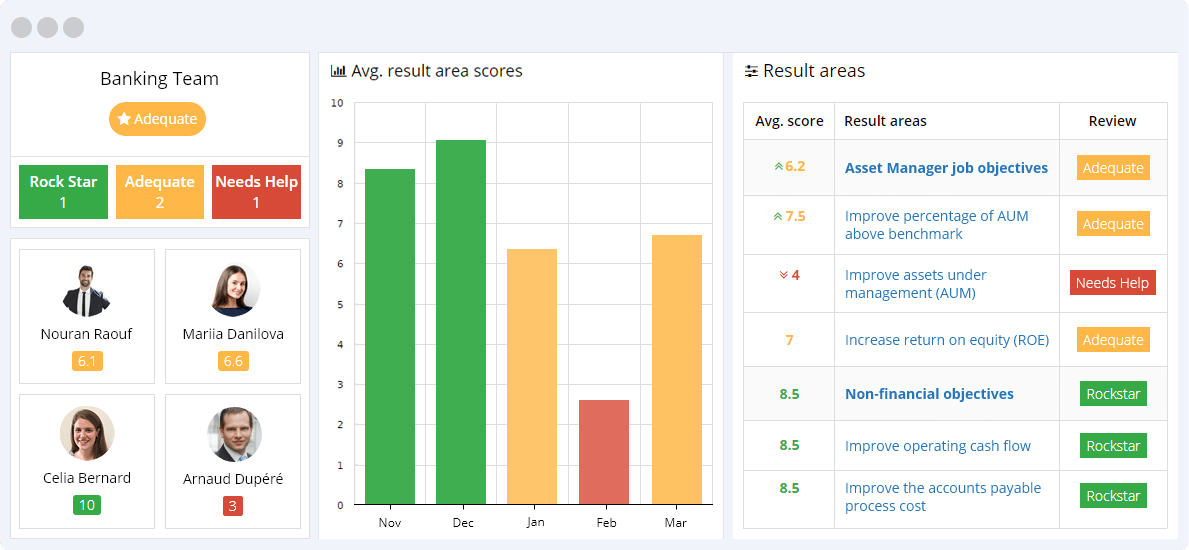
- Improve Assets Under Management (AUM) – The Assets Under Management (AUM) figure is the total market value of the assets managed by the bank on behalf of its clients, including bank deposits, cash, and mutual funds. The higher the AUM value, the greater the banks operating profit generated by the monthly (or annual) AUM fees.
- Improve Percentage Of AUM Above Benchmark – The Percentage Of AUM Above Benchmark metric indicates how your bank’s AUM ranks when compared to its competitors, shown as a percentage. This percentage helps your bank evaluate its performance in relation to its competitors in the banking sector.
- Increase Return on Equity (ROE) – The Return on Equity (ROE) value is calculated as the total income the bank generates divided by the total shareholders’ equity, shown as a percentage. Because the shareholders’ equity equals the bank’s assets minus its debt, the ROE is considered the return on net assets.
- Increase Return on Assets (ROA) – The Return on Assets (ROA) value is the total dollar amount of net income generated by the bank divided by the total assets, shown as a percentage. This percentage demonstrates how profitable the bank is to its total assets, or how the bank uses its assets to generate an income.
View less
Sales Manager Job Objectives
Sales manager objectives are designed to track and measure the sales manager’s role and how efficiently this role’s critical aspects are fulfilled. Core elements, like the management and leadership aspects of this role, are crucial to ensuring an engaged, productive sales team.
- Improve Client Survey Score – The client survey score indicates how well the bank’s employees have performed as measured by customer feedback. Banks send out client surveys at predefined intervals to gather feedback to calculate this score. The higher the score, the greater the bank’s ability to improve the income generated.
- Increase average time to close issues – The average time to close issues is the time it takes for a problem to be solved or closed from when it was first logged. Issues may originate internally (operations, technology) or externally (customers). These issues must be resolved quickly; otherwise, the customer’s perception of the bank will turn negative.
View all
- Improve new account setup error rate – The new account setup error rate is the total number of new customer accounts created that contain one or more errors divided by the total number of new customer accounts set up at the same point in time, shown as a percentage.
- Improve accounts opened with insufficient documentation – The accounts opened With insufficient documentation is calculated as follows: The total number of new accounts opened with insufficient documentation divided by the total number of new accounts opened over the same period, shown as a percentage: the higher this value, the lower the quality of customer service.
- Increase the total volume of accounts – The total volume of accounts is the total number of accounts managed by your bank, tracked by financial timeframes such as money market accounts, long-term deposit accounts, and short-term savings accounts: the higher this number, the greater the potential for generating an income.
- Increase the AUM per employee – The AUM per employee metric is an HR-related metric that helps analyze and manage employee workload. The total value of the bank’s assets is divided by the overall number of employees. A low result shows too many employees, and a high value indicates too few employees to the asset value.
- Increase operating profit per employee – The operating profit per employee is a profitability metric designed to compare income versus the cost of each employee. It is calculated by dividing the total operating profit by the total number of employees. This ratio is often used to compare companies within the same industry.
- Increase sales per branch – The sales per branch metric is the calculated total sales figure for each branch for a predetermined time. This KPI helps management assess which branches or departments are the highest and lowest performing. It is calculated by dividing the gross sales by the total number of branch locations.
View less
Customer Service Analyst Job Objectives
Customer service analysts perform a critical role in the customer support team by collecting and analyzing data like workflow processes implemented, First Call Resolution, and the customer’s lifetime value. These metrics are vital to improving customer service employee effectiveness. This set of KPIs measures the customer service analyst’s job efficiencies.
- The number of workflow processes implemented – The number of workflow processes implemented is the total number of workflow processes implemented during the evaluation period. This is a subjective or retrospective KPI. It is necessary to monitor the number of methods created or revised in order to increase operational efficiencies by implementing workflow processes.
- Improve the Cost to Acquire a Digital Customer [CAC] – The Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the cost of converting a potential customer into a returning customer. It is calculated by dividing the total customer acquisition costs (marketing costs) by the number of new customers acquired during the same time frame.
View all
- Improve the digital traction metrics – Digital traction metrics are KPIs that measure the success of a business in the digital age. These metrics audit the company’s online strategy, whether they helped attain a positive ROI by measuring the brand’s digital platform’s user numbers, ease and frequency of use, and customer engagement levels.
- Improve the lifetime value of a typical customer – The lifetime value of a typical customer is the average time that banking customers stay with the same bank. Banks have an added advantage in that customers do not easily move between banks. Once a customer opens an account, he will stay with your bank for a long time.
- Improve innovation and expansion – The innovation and expansion by a bank are necessary to expand your customer reach and grow your brand’s target audience. This metric measures how innovative your brand is in the context of new financial product offerings; thereby, helping the bank attract and acquire new customers.
- Improve First Call Resolution – The First Call Resolution metric is a vital customer service KPI measurement. The higher the number of queries and problems solved with one call, the higher your bank’s customer satisfaction ratings. It is essential that your customers are satisfied and see that your service team is well-trained and efficient.
View less
Non-Financial Objectives
Non-financial objectives measure the critical efficiencies related to all extra-financial aspects of the business organization. These include customer relationships, quality, operations, cycle-time, and the organization’s sales pipeline. While these objectives are not directly related to the organization’s finances, they are required to contribute to the company’s financial success.
- Improve operating cash flow – The Operating Cash Flow (OCF) shows the total amount of money generated by a company’s daily business operations. This metric measures to what extent the business can maintain the positive cash flow needed to cope with growth and expenses, especially unforeseen and unexpected costs, or whether it requires external financing.
- Improve the current ratio – The current ratio determines whether the asset management company can meet all of its financial obligations in one year. This KPI takes into account the business’s current assets and liabilities, such as account receivables and account payables.
View all
- Improve the quick ratio or acid test – The acid-test ratio demonstrates whether a business has adequate short-term assets to cover its near-future liabilities. The quick ratio provides n accurate overview of a company’s financial health than the current ratio as it ignores liquid assets such as inventories.
- Improve the burn rate – The burn rate reflects the rate at which a company spends money on a weekly, monthly, or annual basis. The faster a company spends money, the higher the burn rate. And if this spending rate is left unchecked and unmonitored, the company incurs the risk of running out of money.
- Improve the net profit margin – The net profit margin demonstrates how efficient the business is at generating a profit compared to its revenue. It is calculated as a percentage of the total revenue over time.
- Improve the gross profit margin – The gross profit margin is a profitability metric that shows the percentage of income left over after the cost of sales has been subtracted. This ratio is a useful indicator of a company’s financial health, indicating whether it can pay for its operating expenses while having funds left for growth.
- Improve working capital – The working capital KPI measures an organization’s assets, such as available cash to meet short-term financial obligations. Apart from available monies, working capital includes short-term investments and accounts receivable, designed to demonstrate the business’s liquidity or ability to source cash quickly.
- Improve the current accounts receivable – The current accounts receivable KPI measures the total monies owed to a business by its debtors. The current accounts receivable metric helps determine future income and calculate the average debtor days, showing how long it takes for a client to pay the amount they owe.
- Improve the current accounts payable – The current accounts payable metric is the opposite of the current accounts receivable. It indicates how much money the business owes to its creditors, including suppliers and banks.
- Improve the accounts payable turnover – The accounts payable turnover indicates the average payable amount that the company pays to its creditors. If the turnover ratio is lower as compared to previous periods, the organization might have trouble paying back its debt. If the turnover rate increases, the organization is paying its suppliers faster than before.
- Improve the accounts payable process cost – The accounts payable process cost demonstrates the total cost of processing all amounts payable during a particular period.
- Improve the accounts receivable turnover – The accounts receivable turnover demonstrates the company’s effectiveness in collecting debts and extending credit. Suppose the business allows a client to increase its amount payable substantially. It is similar to giving away an interest-free loan, instead of using the money to grow the business.
- Improve the inventory turnover – The inventory turnover metric measures how easily the company sells and replaces its inventory over time. It reflects an organization’s ability to generate sales and restock its products to the optimum level.
- Improve the budget variance – The budget variance is a frequently used project management KPI. It measures the extent to which projected budgets vary compared to actual budget totals. The metric evaluates whether the actual expenses or revenue meet the budgeted expectation.
- Improve the budget creation cycle time – The budget creation cycle time is the time taken to research, plan, and agree on a project’s or company’s budget. A long budget creation cycle isn’t necessarily negative, but it might use up valuable resources if it goes on for too long.
- Improve the line items in a budget – The line items in a budget help managers and project leaders keep track of and manage expenditures in a more detailed way. Budgetary line items are accounting measures designed to provide a better overview of company expenses.
- Improve the number of budget iterations – The number of budget iterations translates into the time taken for a budget to be planned, discussed, and approved. The higher the number of budget iterations, the less effective and more time it takes to finalize the budget. The lower the number of versions, the more effective the budgeting process.
- Improve the payroll headcount ratio – The payroll headcount ratio shows how many employees process the payroll related to the company’s total number of employees. This ratio indicates the number of employees in an organization supported per payroll staff member.
- Improve the sales growth ratio – The sales growth ratio demonstrates the change in total sales generated over a specified period. The sales growth ratio shows the percentage of sales in the current period compared to previous periods, indicating whether there has been an increase or decrease in total sales.
- Improve the days’ sales outstanding – The Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) figure displays the average number of days required for clients to pay a company – from the date the invoice has been received to the final payment. The lower the DSO, the more a company can focus on increasing sales and growing its customer base.
- Reduce vendor expenses – The vendor expenses metric shows the current payments the company owes to its vendors or suppliers. High vendor expenses might indicate that the organization is having trouble paying its vendors and suppliers on time.
- Improve the payment error rate – The payment error rate shows the percentage of incoming or outgoing payments that were not completed on time due to a processing error.
- Improve the internal audit cycle time – The internal audit cycle time indicates the average time taken to perform a full internal audit. The longer the time needed, the less organized the organization’s documents are. The shorter the time taken, the more efficient the company’s business processes are.
- Improve the finance error report – The finance error report displays the number of financial reports that require further clarification or contain errors, necessitating a review, and a more detailed investigation.
- Improve the return on equity – The return on equity indicates the capacity of a business to use shareholder’s investments efficiently; thereby, generating high profits. This figure shows how much revenue a company generates for each unit of shareholder equity.
- Improve the debt to equity ratio – The debt to equity ratio is similar to the return on equity metric. This KPI demonstrates the business’s effectiveness at investing its shareholder investments or equity. A high debt to equity ratio indicates that an organization is losing money and accumulating debt instead of generating a profit from existing investments.
- The cost of managing processes – The cost of managing processes KPI measures the time and resources spent on managing and supervising a project. The lower this cost, the higher the number of assets left for implementing additional tasks and growing the business.
- Improve resource utilization – Resource utilization is a metric that indicates whether the company’s employees’ time is being effectively used. Underutilized resources cost money. Employee time is one of the most valuable assets that a company can use to generate an income.
- Reduce the total cost of the finance function – The total cost of the finance function represents the ratio of the total cost of the company’s financial activities compared to its total revenue. An organization’s costs include staff, overhead, and any other expenses necessary for the business’s day-to-day operations.
View less
The bank’s sales department, customer service department, and its asset management department are the three core job roles that drive customers and increase revenue, the elements that drive banking success. Without these three elements working together as a unit, the bank runs the risk of losing money instead of gaining customers and revenue.
Therefore, the customer service analyst, asset manager, and sales manager need to align their visions to streamline the bank’s workflow processes, increase employee output, and manage financial assets to develop and grow income generation activities.
Customer sales efficiencies such as new customer closing rates, the customer survey score, the account set up errors must be tracked and measured to ensure that the sales department prioritizes the need to close new customers and ensure that both existing and new customers remain happy and satisfied.
The customer service division and the asset management department’s roles are crucial to the business. Happy clients remain engaged customers. And customer satisfaction is derived by managing the customers’ financial assets well and treating these clients well.
These banking KPIs are fundamental to understanding the unique relationship between the bank, its financial assets, and the consumer. The KPIs highlight the human resource pain points, the customer relationship difficulties, and any asset management weaknesses to improve job roles and workflow efficiencies. Otherwise, the company runs the risk of having the negatives spiral out of control and cause severe reputational and financial damage.