UX Architect Job Objectives
User Experience (UX) objectives are a set of quantitative and qualitative metrics used to measure, compare, and track the user experience of a website or app over time.
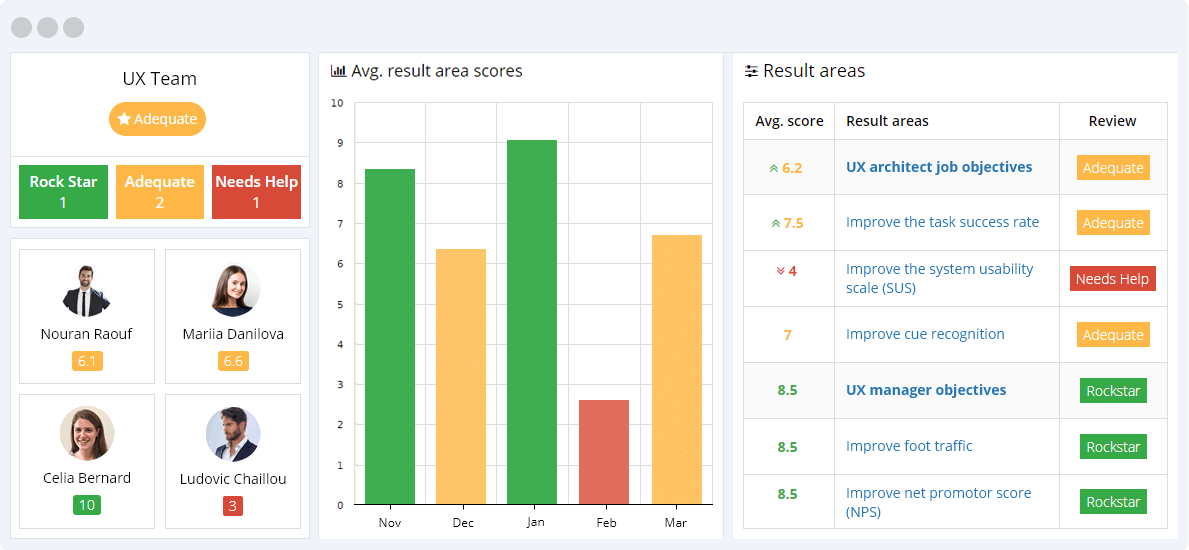
- Improve the task success rate – The task success rate or the task completion rate is the percentage of correctly completed tasks by users on a website or app. It reflects how effectively users can complete predefined tasks. The success rate can be measured as long as the task has a clearly defined goal or endpoint.
- Improve time on task – The time on task measures the amount of time it takes the user to complete a specific task. It is usually expressed in minutes and seconds. And this data is analyzed and presented in different ways, but it is most commonly displayed as the average time spent on each task.
View all
- Navigation versus search – The navigation versus search metric is used to test website or app navigation. The user of the search function requires knowledge of the search space and the correct keywords to use. Users should be able to navigate successfully around a website instead of being forced to use the search function.
- Reduce the user error rate – The user error rate is a useful method to evaluate user performance and success rate. The number and types of errors will tell you how many mistakes were made, at what point they were made, how different designs produce distinctive error frequencies and types, and the overall product’s user experience.
- Improve the System Usability Scale (SUS) – The System Usability Scale (SUS) metric is one of the most widely used tools for assessing a product’s perceived user experience. This KPI is a qualitative metric, and it is based on a survey and not on statistical data. SUS is a way to quantify the qualitative data.
- Improve cue recognition – Cue recognition is designed to provide the users with intuitive clues on how do use or navigate around a product. The user is not required to use recall to navigate around the website or app. The more cues there are, the more usable the product, and the higher the UX.
- Success versus error rate – Success and error rates are an excellent way to evaluate and monitor user performance on your website or product. This metric provides insight into where the product’s weak/strong points are and what the reason for these might be. The higher the success rate, the greater the user experience.
- Navigation functionality – The navigation around a website or app plays a crucial component in directing users through the product while helping them find the information they are looking for. The more natural the navigation around the product, the higher the chance of the user answering the Call-To-Action (CTA).
View less
UX Analyst Job Objectives
The User Experience (UX) analyst extracts and analyses the company’s website’s or app’s UX data to determine the successes and pain points to improve the user experience to increase the visitor numbers that answer the site’s CTA. These KPIs are designed to measure the UX analyst’s role efficiencies.
- Increase customer satisfaction – Customer satisfaction in a user experience context is the extent to which the product’s customers are satisfied with their experience using the product. The most satisfied customers are those who have the best user experience and will reuse the product many times.
- Increase the number of recommendations – Recommendations are an exceptional gauge of UX. A user that has had a great experience is more likely to recommend that product or service to someone else. Consequently, it is no surprise that measuring the likelihood to recommend has become a trend within the business world.
View all
- Improve the usability – A product’s usability is an essential KPI to measure. If the website or app is usable, customers will answer the site or app’s CTA (Call-To-Action) and will convert to return users. Otherwise, the users will navigate away from the brand and to its competitors.
- Improve user ratings – Ratings are a useful way to judge the quality of a product or service. If a product or service has high user-friendliness ratings, users will give it a high score. High ratings translate into increased customer numbers. Consumers use ratings to decide whether to engage with a product or service.
- Improve the user’s ability to complete tasks – Successfully completing tasks is at the heart of user-experience design. A product that doesn’t support the user’s ability to complete their tasks isn’t going to provide an outstanding user experience.
- Improve the user-friendly product descriptions – User-friendly product descriptions are designed to enhance the users’ ability to use the product quickly, easily, and efficiently. If the product descriptions are clunky and incomprehensible, the user will not use the product, costing the company customers and sales.
View less
UX Manager Objectives
User-Experience (UX) objectives are a collection of quantitative metrics used to measure, compare, and track the user experience of a website or app over time. They are critically important for ensuring UX design decisions are made and evaluated using objective evidence rather than subjective opinion.
- Improve foot traffic – UX foot traffic is design paths indicated by the website’s users as the most efficient means of reaching the desired outcome. This is part of the design iteration process, attracting natural user-feedback. This KPI measures the UX manager’s ability to harness this feedback as part of the UX design process.
- Improve UX time on task – The UX Time on Task measures and tracks the time taken for a user to complete a specific task on a website or mobile app. The aim is to reduce the time per task until it reaches its optimal level.
View all
- Improve use of navigation versus search – The user’s ability to navigate around a website rather than use the search function is the preferred navigation mechanism. This KPI measures the extent to which the UX manager tracks this metric when conducting UX design testing.
- Improve (reduce) user error rates – The user error rate metric measures the number of errors a user makes when navigating around a website or app: the lower this metric, the greater the site’s user experience, the greater the chance that its target audience will widely adopt this app or site.
- Improve (reduce) drop-off rates – User-experience drop-off rates are the rate at which the user drops off your company’s website or app. It is a user behavior metric. The lower the drop-off rate, the greater the user experience and the greater the chance the user will answer the site’s CTA.
- Improve conversion rates – A website’s conversion rate measures the number of visitors to the site that answer the site’s CTA and convert into returning customers. The higher this rate, the more successful the product’s user experience. This KPI tracks and measures the UX manager’s ability to ensure that the conversion rate improves regularly.
- Improve Net Promotor Score (NPS) – The Net Promoter Score (NPS) measures the ratio between the number of users that respond positively to the website, the users that are neutral, and the users that respond negatively to the site. The aim is to ensure that most of the website’s users react positively to its user experience.
- Improve System Usability Scale (SUS) – The System Usability Scale (SUS) measures a website’s usability. It also calculates a customer’s user experience. The higher this metric, the more functional the website is and the greater the user experience. This KPI tracks the UX manager’s ability to ensure that the sites SUS is as high as possible.
View less
A website or mobile app presents a brand with a unique opportunity to interact with its target audience on multiple levels. The site or app’s user experience is a critical element of the product’s success. Its aim is to ensure that the user has a premium user experience while navigating the product, entering the sales funnel, and answering the CTA, resulting in the culmination of driving up the company’s sales figures and increasing its profitability metrics.
User experience (UX) Key Performance Indicators are fundamental to understanding the unique relationship between the brand, the product, and the customer. They shine a spotlight on the product’s ease of use, as designed by the UX architect and by the user testing results as analyzed by the UX analyst.
The fundamental reason for the User Experience design and testing KPIs is to measure and track the extent to which the architect and the analyst meet their job expectancies with regards to the analysis and design of a usable and user-friendly product.
Company management is often unaware of the potential disconnect between the UX design and analysis team, website and app developers, and the target audience until the product’s revenue drops or the number of customers answering the CTA drops. These KPIs highlight the potential pain points between these factors before they spiral out of control and cause irrevocable harm to the company-client relationship and its revenue streams.